TRENDING WHITEPAPERS,VIDEOS & MORE

tim
LoanStream Mortgage, the "One" Lender Streamlines the Cluttered Non-QM Space
- Thursday, 11 April 2019


LoanStream Mortgage (LSM) has effectively streamlined its non-prime (Non-QM) offering, into a single loan program. With the release of the "One Program" and the "One Rate Sheet", Broker's and Non-Delegated Correspondents can now quickly and efficiently qualify their borrowers. The new simple program has risk-based adjustments that just make a lot of sense. "Brokers and smaller mortgage bankers are trying to learn these products. When they go to their wholesaler, they get several matrices and rate sheets. It's tough to cut through the clutter and find out where their borrower qualifies or if they will get a better rate in one program or another. Our new 'One Program' solves that issue," said Rabi Aziz, the company's CEO. LSM is also building an internal and external AUS that will be ready for its Underwriters and Brokers in June.
Now a veteran in the non-prime space, LSM has been serving its partners with this product line for over 5 years. Along with the release of the "One Program" were a strong set of guideline enhancements. Amongst the many, some highlights include: New Asset Qualifier Income Program, 1099 Income Program, Business Purpose Qualification Enhancements, Credit Score for Primary Wage Earner, new Business Bank Statement Expense Ratio Option, ITIN's to 85%, Financing for DACA Borrowers, Cash Out for Reserves and many others.
LSM's President Serene Vernon shared in a statement, "We have a dedicated team reviewing internal and external data sources daily, to ensure our product offering is consistently innovative while protecting each borrower it finances by ensuring their ability to repay. Looking at March 2018 compared with March 2019, our non-prime fundings are up 300%. We are grateful to our partners for their business and are looking at every way to streamline the process."
Read more...Housing Sentiment Surges Just in Time for Spring Homebuying Season
- Monday, 08 April 2019

The Fannie Mae Home Purchase Sentiment Index jumped 5.5 points in March to 89.8, reversing last month's slight decline and reaching its highest point since June 2018. Increases in the "Good Time to Buy" and "Good Time to Sell" components drove the measure of consumer sentiment higher, with the two rising 7 and 13 percentage points, respectively. Complementing that rise, more consumers on net expect interest rates to fall within the next 12 months, as that component rose 7 percentage points this month.
"A brighter housing market outlook drove this month's increase in the HPSI – a welcome sign from consumers as we enter the spring and summer home buying seasons," said Doug Duncan, senior vice president and chief economist at Fannie Mae. "The results further corroborate the positive effect of falling mortgage rates on affordability, which we expect will help support a rebound in home sales."
"Continuing a five-month trend, the net share of consumers who believe mortgage rates will go down increased 7 percentage points amid a 35 basis-point drop in mortgage rates in March alone," continued Duncan. "Meanwhile, job confidence – little changed from last month's survey high--also continues to support housing sentiment, while income growth perceptions firmed from both prior month and year-ago levels, potentially supporting an uptick in housing demand. Additionally, consumers appear to have regained some confidence in the housing market, with perceptions of both home buying and home selling conditions returning to their longer-term trends."
HOME PURCHASE SENTIMENT INDEX – COMPONENT HIGHLIGHTS
Fannie Mae's 2019 Home Purchase Sentiment Index increased in March by 5.5 points to 89.8. The HPSI is up 1.5 points compared with the same time last year.
- The net share of Americans who say it is a good time to buy a home increased 7 percentage points to 22%. This component is down 10 percentage points from the same time last year.
- The net share of those who say it is a good time to sell a home increased 13 percentage points to 43%. This component is up 4 percentage points from the same time last year.
- The net share of those who say home prices will go up increased 5 percentage points to 38%. This component is down 4 percentage points from the same time last year.
- The net share of Americans who say mortgage rates will go down over the next 12 months increased 7 percentage points to -45%. This component is up 7 percentage points from the same time last year.
- The net share of Americans who say they are not concerned about losing their job decreased 1 percentage point to 80%. This component is up 9 percentage points from the same time last year.
- The net share of those who say their household income is significantly higher than it was 12 months ago increased 2 percentage points to 20%. This component is up 3 percentage points from the same time last year.
Read more...
A Significantly Improved Appraisal Process Has Reduced the Riskiness of Refinance Mortgages
- Friday, 15 March 2019
By Laurie Goodman and Jun Zhu
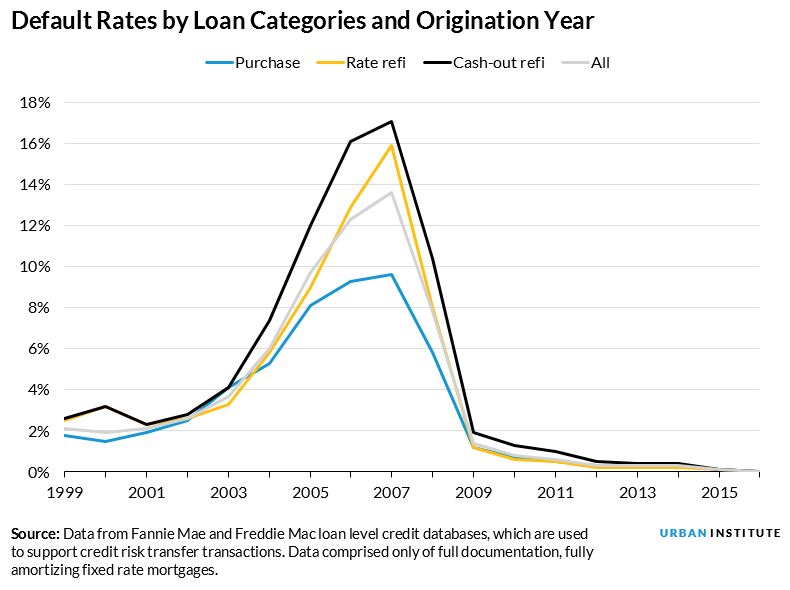
Historically, purchase mortgages have performed better than refinance mortgages, or “refis,” defaulting less often. But changes made in response to widespread appraisal bias during the crisis have improved the industry’s risk assessment and management abilities overall and, accordingly, have decreased the expected default rate on all mortgages.
We looked at the data and concluded that these improvements have reduced the difference in how purchase and refi mortgages perform. And while the models used in FHA, Fannie and Freddie underwriting systems are not public, our results suggest an update may be in order.
Reducing appraisal bias
The pervasive belief that appraisal bias, especially towards no-transaction refinances, was a significant contributor to the great financial crisis lead to a significant re-evaluation of the appraisal process after the crisis. Appraisals undergo much greater scrutiny today, and the GSEs commonly check these numbers against values generated from automated valuation models (AVMs). AVMs use mathematical modeling, drawing on a huge database of recent transactions, complete with property characteristics, to generate an estimated sales prices.
[adbutler zone_id="326314"]
[adbutler zone_id="326316"]
This increased scrutiny has made for more accurate appraisals and the AVMs have enabled Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac to share concerns with lenders about an appraisal prior to the execution of a mortgage, allowing the lender to take corrective action.
It was predicted that these developments would decrease the expected default rate on all refinanced mortgages, which were particularly susceptible to appraisal fraud. The data reveals that this has indeed been the case.
The performance of refis versus purchase mortgages
We examined the characteristics of three broad categories of mortgages:
- Purchase mortgages, which are obtained when a buyer purchases a home
- Rate and term refinance mortgages, which are obtained when a homeowner wants to refinance their home to take advantage of lower rates or to change the length of the mortgage
- Cash-out refinance mortgages, which are obtained when a homeowner wants to tap the equity that has accrued in their home
In an earlier paper, we showed that the risk characteristics of these mortgages—things like loan-to-value ratios (LTV), credit (FICO) scores, debt-to-income (DTI) ratios, and the percentage of owner-occupied loans—did not match the actual performance or default of these mortgages. The loan characteristics indicated that rate and term mortgages would default the least and that cash-out and purchase mortgages should default at about the same rates. But in reality, purchase mortgages defaulted the least, followed by rate and term refis, and then cash-out refis, which defaulted the most.


In other words, the rate and term refinance is riskier for a lender than a purchase mortgage, and a cash-out refinance is the riskiest of all.
But this has been changing (see figure above). The differential between rate and term refinances and purchase loans has been narrowing. This change is exactly what we would expect: as appraisals have become more reliable and AVM models have improved, LTV ratios have become more accurate, and the default differentials have narrowed.
Using regression analyses, we were able to examine the difference in risk characteristics in 2000 to 2009 loans and 2010 to 2017 loans. We learned that the rate and term refinances were 51 percent riskier than purchase loans in the first period but only 11 percent riskier in the more recent period. Cash-out refinances were 96 percent riskier than purchase loans in the earlier period and 55 percent riskier in the more recent period.
In other words, our analysis showed that while the loan characteristics still suggested that cash-out refinance mortgages would be the riskiest and purchase mortgages the least risky, the relative riskiness of the loans had narrowed.
Why do the different default rates between purchase and refinance loans matter?
The GSEs (though Fannie Mae’s Desktop Underwriter and Freddie Mac’s Loan Prospector) and FHA (though is Scorecard) decide which loans to approve using model based inputs on the riskiness of a given set of loan characteristics. Our results suggest that there has been a structural change in the systems which has lowered defaults, especially on refinance loans, and a recalibration of existing models may be order.
Secondly, knowing the default rates for these loans has implications for the proposed capital standards for the GSEs when they emerge from conservatorship (and it has implications for pricing in the interim). Their analysis looks at historical data to determine capital requirements. The standards, as they are currently proposed, require a 1.3 times premium for rate and term refinances and a 1.4 times premium for cash-out refinances.
Our results suggest that the cash-out refinance premium may be fair or a bit low and that the rate and term premium is too high.
A closer look at our methodology
We control for the factors that could drive defaults: LTV ratios, FICO scores, DTI ratios, interest rates, loan balances, and indicators for single-family, owner-occupied, and issue years. We also include an indicator for rate and term refinances and another indicator for cash-out refinances. Purchase loans are served as the reference category.
About the Authors:
Laurie Goodman is a vice president at the Urban Institute and codirector of its Housing Finance Policy Center, which provides policymakers with data-driven analyses of housing finance policy issues that they can depend on for relevance, accuracy, and independence.
Jun Zhu is a senior research associate in the Housing Finance Policy Center at the Urban Institute. She designs and conducts quantitative studies of housing finance trends, challenges, and policy issues.




